-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
4) The select method
Ana Paula Oliveira de Lima edited this page Nov 10, 2021
·
1 revision
The select method is called to select data in the database. It receives as a parameter an object containing the data to be selected and always return an object with the fields data and error . The method is asynchronous and its use must be done using async await or promises.
The select method receives as a parameter an object with the following keys:
-
table: string with the value of the name of the table on which the select will be made; -
columns: array containing the name of the columns to be selected; -
where(optional): object. Each key of the where object will be the name of the column that will compose the conditions of the where clause, this key that take the name of the column will be an object containing the following keys:-
operator: string with the name of the operator that will be used. Accepted values: =, !=, <, >, <=. >=, is, is not, in, not in, like, ilike, not like, not ilike, between and not between; -
value: integer, string, or array containing the value the operator references. Pass values as arrays only when making use of the in, between, not in and not between operators; -
percent(optional): when making use of the operatorLIKEand derivatives, thepercentkey can be included. It indicates where the wild card%will be. Accepts the valuesstart, forLIKE ‘%foo’,endforLIKE ‘foo%’andbothforLIKE ‘%foo%’. ForLIKE ‘foo’, thepercentkey can be omitted.
-
-
logicalOperators(optional): array containing the logical operators of the where clause in the order they should be put according to the order of the columns in the where object. If where has only one column, logicalOperators is not needed. -
join(optional): object. Each key of this object will be the name of a table that will compose the join. This keys also store an object, in turn, containing the following keys:-
join: stores a string with the join type to be performed on that table. Accepted values: JOIN, INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN and FULL OUTER JOIN, case insensitive. -
on: stores an object whose keys are the name of a column of the new join table. This keys are also storing objects. The last ones will be objects containing the following keys:-
operator: string with the name of the operator that will be used. Accepted values: =, !=, <, >, <=. >=, is, is not, in, not in, like, ilike, not like, not ilike, between and not between; -
value: integer, string, or array containing the value the operator references. Pass values as arrays only when making use of the in, between, not in and not between operators; -
percent(optional): when making use of the operatorLIKEand derivatives, thepercentkey can be included. It indicates where the wild card%will be. Accepts the valuesstart, forLIKE ‘%foo’,endforLIKE ‘foo%’andbothforLIKE ‘%foo%’. ForLIKE ‘foo’, thepercentkey can be omitted.
-
-
logicalOperators(optional): array containing the logical operators in the order they should be put according to the order of the columns in theonobject. Ifonhas only one column, logicalOperators is not needed.
-
-
groupBy(optional): array containing the name of the columns by which the selection should be grouped; -
orderBy(optional): array containing the name of the columns by which the selection should be ordered; -
having(optional): object containing the following keys:-
columns: stores an object whose keys will be the name of a column. This keys, in turn, will be objects containing the following keys:-
operator: string with the name of the operator that will be used. Accepted values: =, !=, <, >, <=. >=, is, is not, in, not in, like, ilike, not like, not ilike, between and not between; -
value: integer, string, or array containing the value the operator references. Pass values as arrays only when making use of the in, between, not in and not between operators; -
percent(optional): when making use of the operatorLIKEand derivatives, thepercentkey can be included. It indicates where the wild card%will be. Accepts the valuesstart, forLIKE ‘%foo’,endforLIKE ‘foo%’andbothforLIKE ‘%foo%’. ForLIKE ‘foo’, thepercentkey can be omitted.
-
-
logicalOperators(optional): array containing the logical operators in the order they should be put according to the order of the columns in thecolumnsobject. Ifcolumnshas only one column, logicalOperators is not needed.
-
See a generic example of this structure:
{
table: "table_name",
columns: ["column1", "column2"],
where: {
coulumn_name: {
operator: "operator",
value: ["value"] || 1 || “value”,
percent: “start" || “end" || “both",
},
},
logicalOperators: ["AND"],
join: {
tableToJoin: {
join: "join type",
on: {
tableToJoinColumn: {
operator: "operator",
value: ["value"] || 1 || “value”,
percent: “start" || “end" || “both",
},
},
logicalOperators: [“OR"],
}
},
groupBy: ["columnName", "columnName2"],
orderBy: ["columnName", "columnName2"],
having: {
columns: {
columnName: {
operator: "operator",
value: ["value"] || 1 || “value”,
percent: “start" || “end" || "both"
},
},
logicalOperators: [“AND"],
}
}
Below is an example of using the select method:
Given the table users:
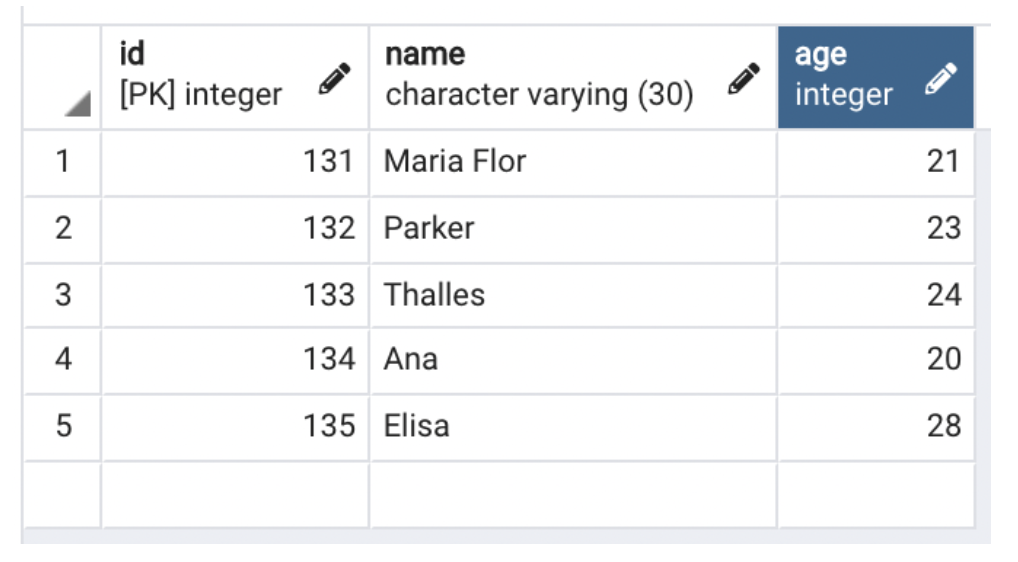
We will make the select below:
const select = {
table: "users",
columns: ["*"],
where: {
id: {
operator: ">=",
value: 133
}
},
logicalOperators: [],
orderBy: [“id desc"],
}
// async await
const selectResult = await query.select(select);
// promise
query.select(select)
.then( (result) => res.send(result.data))
.catch( (error) => res.send(error));
The select method will always return an object with the following keys:
-
data: array containing the selection result, if the selection fails, data will be false; -
error: object containing the transaction and passing parameters errors occurred during transaction.
See below the return of the select mede earlier:
{
error: {
transaction: false,
params: false
},
data: [
{ id: 135, name: 'Elisa', age: 28 },
{ id: 134, name: 'Ana', age: 20 },
{ id: 133, name: 'Thalles', age: 24 }
]
}
© 2021-Ana Paula Oliveira de Lima
All rights reserved